This thesis explores the career experiences of women civil engineers in the UK and examines how women negotiate their place in a highly male-dominated profession. The thesis considers why women are under-represented in this profession, are rarely appointed to senior management positions and how changes in the business pattern of UK engineering consulting companies has created barriers or opportunities for women. Uncovering the detail of women’s career expectations and experience was more suited to a qualitative approach to data collection. .A series of semi-structured interviews was carried out with thirty-one women engineers working in different sectors of the profession. The women were in a variety of personal circumstances, including single and married women, some with young children and others with no dependent caring responsibilities. The ages of the women ranged from twenty three to fifty six years with the majority having attained chartered status. The interviews focused on factors that affect career progression and these were discussed within the three themes of subcultures of the profession, work/life balance and possible agents for change. Quantitative membership data from the Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) and other construction professions has been analysed to provide the context for the research. Feminist concerns about the relationship between women’s role in the private sphere of the home and the public sphere of paid work have led to a theoretical framework that draws mainly on the work of Walby and Cockburn. This has been enhanced by Greed’s gendered critique of the wider construction sector. The findings show that women feel isolated within the profession and t his isolation seems more pronounced for the few women who reach the top and also generally in the setting of the construction site. Despite attempts by some contracting firms to reform the culture of construction sites, this sense of isolation is heightened by problems of harassment in that setting. .Thus, for many women the prospect of working on site is still very daunting. .Equal opportunities policies have a low profile in the industry and this research shows that women working as professionals in construction do not see’ equality’ measures of this type as likely agents for change. The image of the profession as predominantly a ‘male preserve’ continues. and the ICE is regarded as a ‘very male club’ which admits women only reluctantly. Although women report feeling marginalised within the profession many receive personal support from individual male and female colleagues and this factor can be critical to their career progress. Moving into management is seen as necessary for career success but some women are ambivalent about the negative impacts this may have on work/life balance. The culture of long hours is dominant and this marginalises women with caring commitments and reinforces male hierarchy within the profession.
Search Results for “Efficient 300-740 Flexible Learning Mode | 300-740 100% Free PDF Download 🥏 Copy URL 「 www.pdfvce.com 」 open and search for ➤ 300-740 ⮘ to download for free 🤬Valid 300-740 Mock Test”
ABC participated in the BPS Cyberpsychology #CyberSectionChat on the topic of Cyberbullying this month.
The British Psychology Society (BPS) Cyberpsychology (@BPSCyberPsych) section discusses various ‘cyberpsychology’ related topics each month for their #CyberSectionChat. Researchers and industry advocates who study the application of psychology to digital technologies and the Internet (cyberpsychology) tweet about their views, tips and research/industry/practitioner experience during the chat. January’s topic was on Cyberbullying, and ABC were delighted to be involved.
The chat consisted of tweeters addressing 6 questions about cyberbullying: 1) Should cyberbullying and traditional bullying be seen as separate phenomena? 2) What is the most serious societal or individual level impact of cyberbullying? 3) Who is most likely to be targeted for cyberbullying? Are all age groups vulnerable in the same ways? 4) What are the shortcomings in cyberbullying research that should be prioritised in future? 5) What are the key barriers to addressing cyberbullying? What interventions could address these? and 6) How can we increase resilience to cyberbullying?
Dr. Dawn Branley-Bell of Northumbria University tweeted on the characteristics that might distinguish ‘traditional’ bullying from cyberbullying.
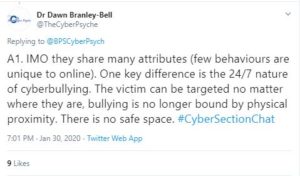
Dr. Peter J. R. Macauley, lecturer in social psychology at Staffordshire University, tweeted about the negative consequences of cyberbullying for all involved addressing the individual and the wider society.
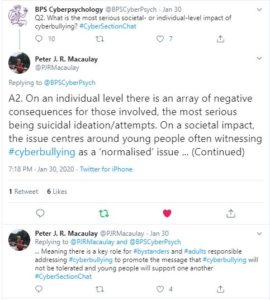
Dr. Maša Popovac, lecturer at the University of Buckingham tweeted on some of the ways resilience to cyberbullying could be promoted via digital citizenship and online safety education.
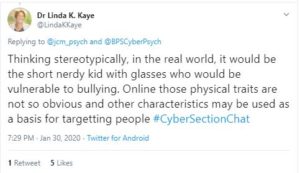
Dr. Linda Kaye, senior lecturer at Edge Hill University commented on how the dynamics of online spaces can change how bullies target victims differently to how they would in ‘traditional bullying’.
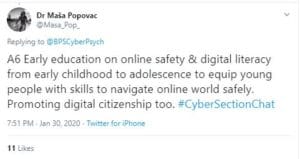
It was also important to critique some of the ways that researchers measure cyberbullying, particularly in relation to quantitative measures that are widely used. So ABC did just that.
There were other fantastic tweets from other contributors too – apologies for not mentioning them all here! It was certainly stimulating to discuss such issues in relation to cyberbullying and engage with researchers who follow similar interests in promoting online safety, and making the online world a safer place for all concerned. ABC expresses many thanks to the committee behind BPS Cyberpsychology who organised the chat (also ABC won a contributor award XD). To visit the #CyberSectionChat, readers can access all of the tweet contributions on Twitter here.
Policy-making and service development tends to what has been called the ‘ideal of impartiality’ whereby difference between different population groups is reduced to unity. At the same time, inherent within equality law is an understanding that the population is heterogeneous, experiencing complex forms of injustice which require the opportunity for legal redress. The Equality Act 2010 includes a general duty on public authorities, the Public Sector Equality Duty (PSED), to have due regard to eliminate unlawful discrimination, harassment and victimisation, advance equality of opportunity and foster good relations between different groups in relation to nine protected characteristics. Secondary legislation in Scotland has added significant additional requirements with the potential to transform the way that public authorities think and act about equality including duties to report progress on mainstreaming the equality duty, to publish equality outcomes and report progress and to assess and review policies and practices. The way that this secondary legislation has been
conceptualised, interpreted and how it has informed planning and practice within public authorities has not previously been the subject of a body of research. This thesis has sought to contribute to greater understanding about the potential of the PSED in Scotland by applying interpretive policy analysis to the application of the duty in one city, Glasgow. Interpretive approaches to policy focus on meanings that shape actions and institutions and draw on a range of methods to follow the objects, the language, the relevant actors and the acts
associated with the policy. Within this context, an assumption has been made that a compound narrative about injustice, equality as constitutive of social justice and institutional change within the city can be derived by investigating meaning and action associated with the PSED from a number of different perspectives. Firstly, the framing and the discourses associated with formal texts required for compliance produced by five key institutions with responsibility for different facets of city life have been investigated critically. These five institutions are
the Scottish Government, Glasgow City Council, the Glasgow Health and Social Care Partnership, NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde and the City of Glasgow College, selected for both their relationship to social structures which determine equality and for their responsibilities for its different dimensions. Secondly, the perspectives of three communities of meaning – those directly responsible for compliance, those indirectly responsible for compliance and advocates for social groups – have been gathered through the use of semi-structured interviews in order to compare and contrast their interpretations with the formal texts. Lastly, the meaning and actions associated with the mainstreaming requirement of the secondary duties have been considered in order to ascertain whether and how equality aspirations have shaped the strategic and operational responsibilities of Glasgow City Council, health and social care provision and further education in the city in relation to theories of urban justice. The PSED was largely viewed as an important and beneficial piece of law, that there was no room for
discrimination within the city and that equality across different social groups was an acceptable ideal. The duty was also viewed as a means of exerting pressure on public institutions both from within and from the outside to reflect on the meaning of equality and to consider the way that organisations both perpetuated and resolved inequality. At the same time, the opportunities afforded by the secondary duties to transform social systems and dimensions of equality were not met and as a consequence the potential for Glasgow to be a more just city for its heterogeneous population not realised.
Workplace bullying is an issue of practical importance and theoretical interest. Not only is workplace bullying of increasing concern to employers and employees, it is also the focus of empirical research and analysis. However, there are few studies which examine workplace bullying in Turkey. This study aims to investigate the nature of bullying in Turkish workplaces and to examine the association of bullying with paternalistic leadership and various work-related attitudes. The study uses both qualitative and quantitative techniques. Twenty-eight semi-structured interviews were conducted with Turkish employees to explore in depth the nature of workplace bullying, with a thematic analysis indicating that polarisation at work and institutionalised bullying were major problems in Turkish organisations. In the second phase of the study, a questionnaire focusing on the nature of bullying and its potential determinants was completed by employees in both the public and private sectors in Turkey (n=142). Findings from both the interview study and an exploratory factor analysis of the questionnaire data were used to adapt the Negative Acts Questionnaire-Revised (NAQ-R) for use in Turkey. In the final stage, the adapted questionnaire was completed by a sample of public and private sector employees in Turkey (n=708). Confirmatory factor analyses were used to examine the components of bullying and their relation with dimensions of paternalistic leadership. Hierarchical regression analyses revealed that loyalty-seeking paternalism is positively related to the experience of bullying, whereas familial paternalism is negatively related to the experience of bullying. In addition, negative associations were observed between organisation-based selfesteem and all the components of bullying, except for experience of non-work related criticism. Finally, intention to leave was found to be positively associated with experience of task pressures and work related criticism. This study contributes to the bullying literature by exploring the nature of workplace bullying in Turkey using complementary methods.
Social media and communication technology has completely transformed the way that individuals, communities and organizations share and create information. The interactivity, accessibility and usability of social media in particular has made it an extremely popular utility. Political campaigns, celebrity promotions and news disseminations have utilised social media to share important information and raise the awareness of key social issues. Despite this, social media and communication technology also has a great deal of potential to do harm. For example, in 2013, Reddit admitted that their platform had contributed to online witch hunts when groups of users had wrongly named people as suspects in the Boston bombing (Messing & Westwood, 2012). The ease at which individuals can share content also poses risks, with a large potential for the sharing of undesirable material. A survey of 10,000 European children between the ages of 9 and 16 years, reported that 40% of children expressed shock and disgust after being sent violent or pornographic content (Livingstone, Kirwil, Ponte, & Staksrud, 2013). Social media can also contribute to acts of cyberbullying, stalking, and online harassment (Kwan & Skoric, 2013); estimates suggest that 10-40% of youth are victims of cyberbullying (Kowalski, Giumetti, Schroeder, & Lattanner, 2014), and 40% of those who cyberbully report they do so for fun (Raskausas & Stoltz, 2007; Chou & Edge, 2012). Campaigners have called for greater guidance concerning the way communication technology is used, with calls for stricter legislation (NSPCC, 2017). However, at present there is limited research exploring the association between cybervictimization and mental health, particularly in adults. Cybervictimization experiences have many different components. This thesis aims to further explore this and add to the existing evidence base, with a particular focus on cyber harassment of a sexual nature. This review will consist of two chapters. The first chapter will be a systematic review, aimed at exploring the psychological impact of all forms of cybervictimization in adults. The second chapter will specifically explore the effects of cybersexual harassment, with a view to better understanding its associations with anxiety, depression, body image, and trauma.
The transition to secondary school can be a period of excitement and apprehension for all children; however increased anxiety surrounding change can make periods of transition challenging for children with an autistic spectrum condition (ASC) and can affect their ability to adapt to the new social and physical environment. This study explored the experiences of eight children with ASC during the transition to secondary school. Children were interviewed towards the end of the summer term at primary school and during the first term at secondary school. Children’s drawings and models were used to facilitate the interview process and as a focus for discussion. Findings suggest that some of the aspects of transition experienced by children with ASC are common to all children moving from primary to secondary school, such as familiarisation with the school environment, social relationships, fear of bullying, looking forward to new subjects and people, and new opportunities. However, some of the children in this study experienced heightened anxiety, particularly pre-transition when they were uncertain what to expect, how other children would react to them, who they should make friends with and what they would do if they had difficulty managing their emotions. Induction visits successfully addressed some of these issues however most children still experienced uncertainty about some aspects of secondary school. In contrast, familiarity with the new environment and a greater degree of predictability about the structure of the school day in addition to knowing school staff and making new friends contributed to children’s positive emotions about school. There were some aspects of transition that children felt could be improved such as preparation, peer support, preventative support from teachers and the opportunity to talk about transition and social and emotional issues. Findings emphasise the importance of adequate preparation and individualised planning involving children in the process.
This thesis investigates cognitive mechanisms underlying youths’ vulnerability for involvement in bullying and developing adjustment problems. The aim of this thesis was threefold: (1) investigate whether early cognitive functioning acts as a developmental marker for children’s later involvement in bullying; (2) investigate the cognitive processing of bullied children and whether these skills were associated with adjustment problems; (3) investigate whether early cognitive functioning acts as a differential marker for bullies and non-bullies who have other antisocial behaviour problems. Participants were members of the Environmental-Risk (E-Risk) Longitudinal Twin Study, a nationally representative sample of 2,232 children and their families, and the Dunedin Multidisciplinary Health and Development Study, a longitudinal birth cohort of 1037 children born in Dunedin, New Zealand. Using multiple informant reports, measures of bullying, antisocial behaviours, cognitive functioning, child-specific and family factors were collected during childhood, adolescents and adulthood. Poor theory of mind (ToM) in early childhood predicted becoming a victim or bully-victim in adolescence over and above child-specific and family factors. For bullies, the risk of having poor ToM was overridden by socioeconomic deprivation and child maltreatment. Bullied children reported biased interpretation of their environments when compared to their non-bullied co-twin. Children who used biased attribution styles when interpreting the cause of negative events had higher levels of adjustment problems. Bullies did not differ in their early cognitive processing, temperament and family environment from children with high antisocial behaviours, but did from children with moderate antisocial behaviours. Being a bully or having antisocial behaviours predicted adjustment problems in adolescence and adulthood. Being a bully had an independent effect on substance use in adolescence and emotional problems in adulthood over and above the risk posed by having antisocial behaviours. Findings from this thesis identify cognitive functioning as an early developmental marker for children’s involvement in bullying and a mechanism that may be negatively affected by children’s bullying experiences. Supporting positive cognitive development throughout childhood may help to reduce children’s risk of being involved in bullying and maintain healthy cognitive processing techniques that promote mental wellbeing.
Bullying in schools is a growing international concern as the consequences of bullying and victimisation have been shown to be far-reaching. With the aim of developing effective anti-bullying interventions, previous research has investigated. The factors situated within the child’s family and within the child themselves that are considered to be the causes of childhood bullying. An underdeveloped area in the literature was in relation to the protective characteristics of children who are at risk of bullying, specifically how the characteristics of children mediate or moderate the effects of negative family experiences on bullying behaviours.